- Find A Medical Provider
- Auto Injuries
- Common Injuries
- Medical/Pharmaceutical
- Types of Medical Injuries
- Malpractice Injuries
- Drug and Medical Device Injuries
- Drugs and Devices Linked to Cancer
- Opioid Addiction
- Drugs and Devices Known to Cause Injury
- 3M Combat Arms Earplugs – Hearing Loss
- Accutane
- Aciphex
- Actonel
- Actos
- Adderall and Ritalin
- Advair
- Aldara (Imiquimod)
- Alli
- Ambien
- Amiodarone
- Anzemet
- Aptivus
- Aranesp
- Arava
- Atorvastatin
- Avandia
- Benicar
- Birth Control Medication
- Blood Thinners
- Essure
- Fosamax (Alendronate Sodium)
- Gadolinium-Based MRI Contrast Agents
- Granuflo
- Hernia or Surgical Mesh Injuries
- Hydroxycut
- Inferior Vena Cava Filters
- Invokana Toe and Foot Amputations
- Ketek
- Levaquin
- Lipitor
- Mirapex
- Neurontin
- Onglyza
- Over-the-Counter Medications
- OxyContin
- Paxil
- Power Morcellators
- Pradaxa
- Propecia
- Reglan
- Talc Powder
- Trasylol
- Valsartan
- Viagra
- Xolair
- Zelnorm
- Zoloft
- Work Injuries
- Sports Injuries
- Marketing Services
- Blog
List your practice on InjuredCare | Log in / Sign up
Cuts and Lacerations
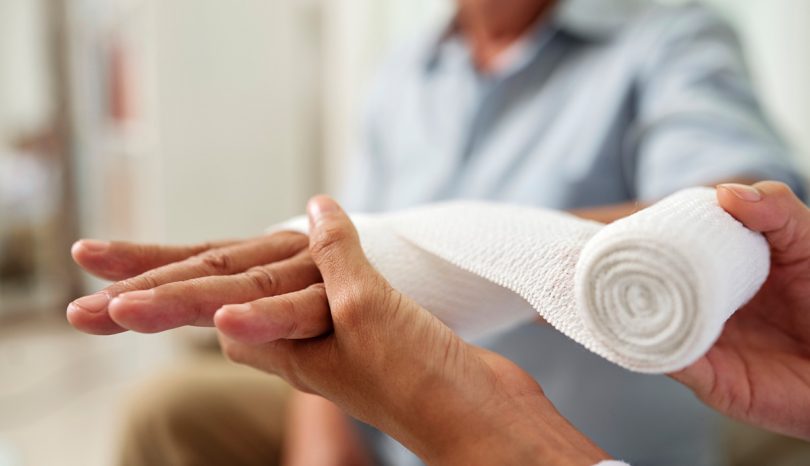

Cuts and lacerations are common injuries in the workplace, and the reasons behind these mishaps vary. Injuries may occur due to improper training, a lack of established safety procedures, not paying attention, failure to wear proper hand protection, or missing or improperly adjusted safety equipment.
Avoiding Cuts and Lacerations
Workplace safety procedures — and following those recommendations — are the easiest way to avoid injuries. A safety plan should include:
- Wearing personal protective equipment (PPE), including eye protection, gloves and long sleeves. Employers should work with employees to determine the proper fit and style of gloves, depending on the job.
- Keeping the work area clean.
- Using a sharp blade if blades are used. A dull blade means a worker must exert more force when cutting, increasing the risk of injury. Replace dull blades when necessary.
- Not leaving exposed blades unattended. Consider the use of self-retracting cutting blades.
- Using cut-resistant gloves where needed.
How to Treat Injuries
In case of an injury, because cuts are prone to infection, clean the wound thoroughly. Place the wound under running water and clean it for approximately five minutes with soap and water.
For more severe cuts, the first step is to stop the wound from bleeding excessively by applying direct pressure. If direct pressure doesn't stop the bleeding, go to your local emergency room or contact a medical provider for care. Immediately seek emergency care if a wound is on the head, chest or stomach, unless the wound is very small.
For any wound that shows signs of infection, such as redness, swelling or draining pus, consult a medical professional.