- Find A Medical Provider
- Auto Injuries
- Common Injuries
- Medical/Pharmaceutical
- Types of Medical Injuries
- Malpractice Injuries
- Drug and Medical Device Injuries
- Drugs and Devices Linked to Cancer
- Opioid Addiction
- Drugs and Devices Known to Cause Injury
- 3M Combat Arms Earplugs – Hearing Loss
- Accutane
- Aciphex
- Actonel
- Actos
- Adderall and Ritalin
- Advair
- Aldara (Imiquimod)
- Alli
- Ambien
- Amiodarone
- Anzemet
- Aptivus
- Aranesp
- Arava
- Atorvastatin
- Avandia
- Benicar
- Birth Control Medication
- Blood Thinners
- Essure
- Fosamax (Alendronate Sodium)
- Gadolinium-Based MRI Contrast Agents
- Granuflo
- Hernia or Surgical Mesh Injuries
- Hydroxycut
- Inferior Vena Cava Filters
- Invokana Toe and Foot Amputations
- Ketek
- Levaquin
- Lipitor
- Mirapex
- Neurontin
- Onglyza
- Over-the-Counter Medications
- OxyContin
- Paxil
- Power Morcellators
- Pradaxa
- Propecia
- Reglan
- Talc Powder
- Trasylol
- Valsartan
- Viagra
- Xolair
- Zelnorm
- Zoloft
- Work Injuries
- Sports Injuries
- Marketing Services
- Blog
List your practice on InjuredCare | Log in / Sign up
Burns
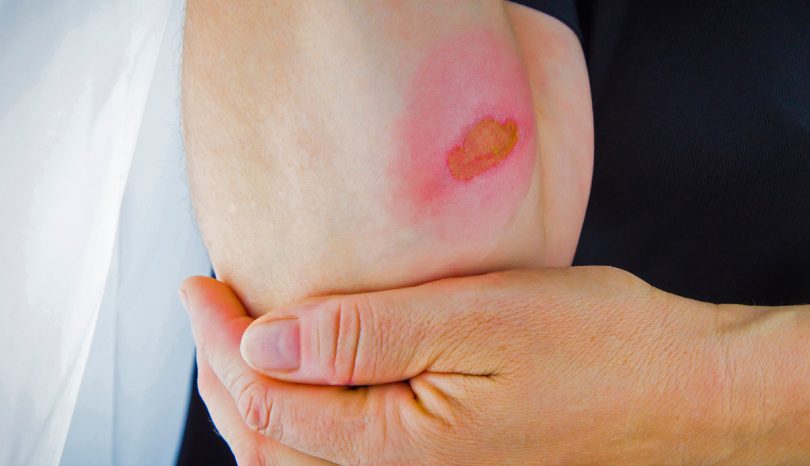
A burn is an injury commonly caused by excessive heat or cold, electricity, radiation or chemicals. In 2007, medical professionals treated approximately a half million burn cases. Most burns are caused by exposure to fire or a hot gas or liquid, such as boiling water. Children are particularly at risk for accidental thermal burns.
Burns are classified in degrees from one to three. A first-degree burn affects only the outer layer of skin and can be treated at home by running cool water on the area and taking a pain reliever. Symptoms include redness, pain and minor swelling.
A second-degree burn requires medical attention as soon as possible. Clothing that is stuck to the skin should not be removed, and the affected area should be elevated above the heart. Additionally, applying a cool compress to the area and taking pain relievers will soothe the pain. Symptoms include redness, severe pain and blisters.
Third-degree burns are serious and even life-threatening. These burn patients remain in the hospital for several weeks. Cosmetic or reconstructive surgery might be necessary to improve both the appearance and the function of the burned area. Symptoms include a dry surface area that is white and waxy, brown, leathery or charred. Because of the severe nerve damage associated with such burns, the victim might feel little or no pain initially.
Source Information:
American Burn Association. "Burn Incidence Fact Sheet." 2016.