- Find A Medical Provider
- Auto Injuries
- Common Injuries
- Medical/Pharmaceutical
- Types of Medical Injuries
- Malpractice Injuries
- Drug and Medical Device Injuries
- Drugs and Devices Linked to Cancer
- Opioid Addiction
- Drugs and Devices Known to Cause Injury
- 3M Combat Arms Earplugs – Hearing Loss
- Accutane
- Aciphex
- Actonel
- Actos
- Adderall and Ritalin
- Advair
- Aldara (Imiquimod)
- Alli
- Ambien
- Amiodarone
- Anzemet
- Aptivus
- Aranesp
- Arava
- Atorvastatin
- Avandia
- Benicar
- Birth Control Medication
- Blood Thinners
- Essure
- Fosamax (Alendronate Sodium)
- Gadolinium-Based MRI Contrast Agents
- Granuflo
- Hernia or Surgical Mesh Injuries
- Hydroxycut
- Inferior Vena Cava Filters
- Invokana Toe and Foot Amputations
- Ketek
- Levaquin
- Lipitor
- Mirapex
- Neurontin
- Onglyza
- Over-the-Counter Medications
- OxyContin
- Paxil
- Power Morcellators
- Pradaxa
- Propecia
- Reglan
- Talc Powder
- Trasylol
- Valsartan
- Viagra
- Xolair
- Zelnorm
- Zoloft
- Work Injuries
- Sports Injuries
- Marketing Services
- Blog
List your practice on InjuredCare | Log in / Sign up
Repetitive Strain Injury (not carpal tunnel)
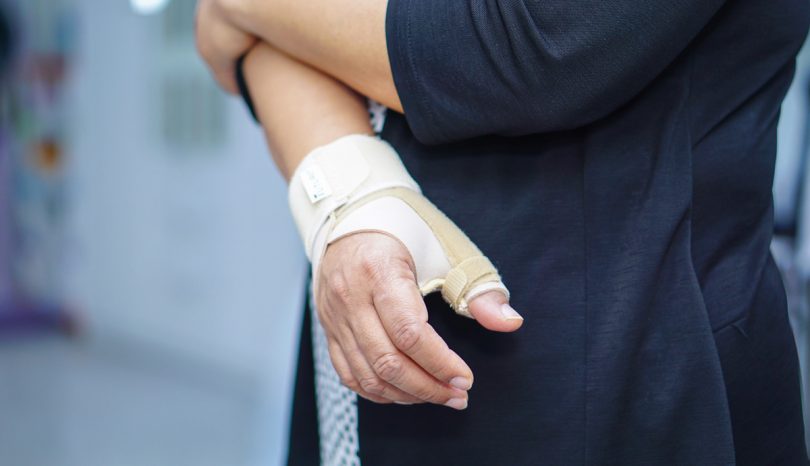

Injuries from sprains and strains affect millions of U.S. workers each year. One type of injury is a work-related musculoskeletal disorder, often referred to as repetitive strain injury (RSI). These injuries are caused by repetitive tasks, forceful exertions, vibrations, mechanical compression or sustained or awkward positions.
Symptoms of RSI include aching, pulsing pain, tingling or extremity weakness commonly affecting a person's arms, hands, shoulders or neck.
Starting with diagnostic imaging testing such as an MRI, a chiropractor or other medical professional can evaluate the full extent of an RSI to make treatment recommendations. Usual treatment may include a method known as RICE — rest, ice, compression and elevation — or physical therapy to help a patient regain the full range of motion that existed before the injury occurred. In more severe cases, surgery could be the answer. Additional treatment options include biofeedback, ultrasound therapy, relaxation, or medication for early-stage RSIs including analgesics.
Also, to decrease the risk of developing RSI or preventing further injuries, medical professionals may recommend specific strengthening exercises to improve sitting posture or other modifications of posture or arm use.